Car Waale
Team name: Hackerman-101
Team members
- Jainam Dharod - j.dharod1238@gmail.com
- Riya Samel - samelriya40@gmail.com
- Aryan Nikam - aryannikamthe1@gmail.com
- Yash Mastud - mastud.yash7@gmail.com
Mentors
- Mentor- Anuj Raghani
- Mentor- Owais Hetavkar
- Mentor- Hrim Gandhi
Description
-
This is a web application that gives you information about a car, just from its image.
-
The app uses machine learning(CNN) to identify the car from its image by splitting the image in parts and using those parts get results.CNN image classifications takes an input image, processes it and classifies it under certain categories.

- First to train the ML program to identify images, we use a dataset with preferably a large number of images. From these images we first identify the part that contains the car in it.
def save_train_data(fnames, labels, bboxes):
src_folder ="/content/Hackerman-101/dataset/cars_train/cars_train/"
num_samples = len(fnames)
train_split = 0.8
num_train = int(round(num_samples * train_split))
train_indexes = random.sample(range(num_samples), num_train)
pb = ProgressBar(total=100, prefix='Save train data', suffix='', decimals=3, length=50, fill='=')
for i in range(num_samples):
fname = fnames[i]
label = labels[i]
(x1, y1, x2, y2) = bboxes[i]
src_path = os.path.join(src_folder, fname)
src_image = cv.imread(src_path)
height, width = src_image.shape[:2]
# margins of 16 pixels
margin = 16
x1 = max(0, x1 - margin)
y1 = max(0, y1 - margin)
x2 = min(x2 + margin, width)
y2 = min(y2 + margin, height)
# print("{} -> {}".format(fname, label))
pb.print_progress_bar((i + 1) * 100 / num_samples)
if i in train_indexes:
dst_folder = '/content/working/data/train/'
else:
dst_folder = '/content/working/data/valid/'
-
These images are then processed to isolate the part that contains the car, ignoring the surroundings, for better results.
-
These are then passed through a Convolutional Neural Network(CNN), to train it or an already trained network can be used. We used an existing Keras EfficientnetsB3 model and trained it on our dataset for ideal results.
model = Sequential()
efficientnetB3 = EfficientNetB3(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=(299,299,3))
for layer in efficientnetB3.layers[:30]:
layer.trainable = False
model.add(efficientnetB3)
model.add(AveragePooling2D(5,5))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dropout(0.7))
model.add(Dense(196,activation="softmax"))
-
We then used Flask for backend app development and HTML and CSS for frontend.
-
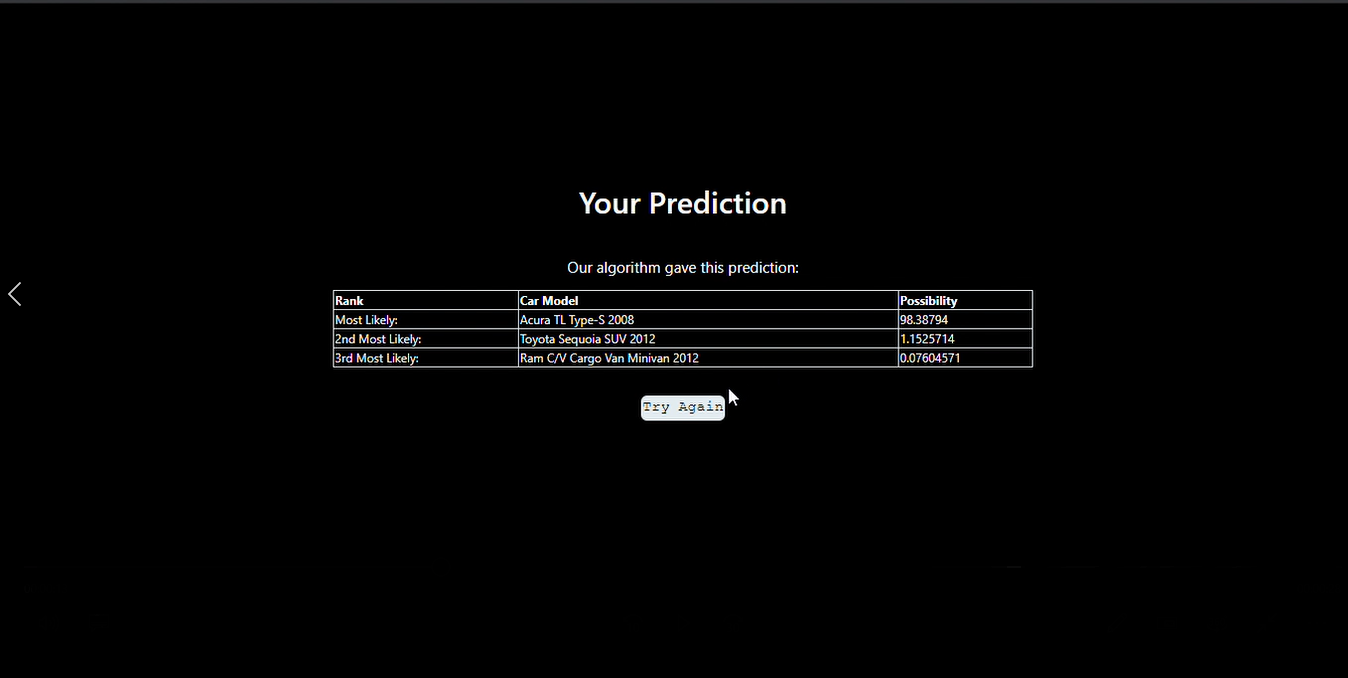
The trained model is loaded into the Flask program, the uploaded image is passed through this model to get the name of the car.
global sess
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.set_session(sess)
global model
model = load_model('C:/Users/samel/OneDrive/Desktop/testing/Finalmodel.h5')
global graph
graph =tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph()
- GitHub repo link: Link to repository
- Drive link: Drive link here
Technology stack
- Machine Learning
- Flask
- HTML
- CSS
Project Setup
- Clone our github repository on your local machine.
- Have Python installed on you machine, Python 3.6.8 works best. Ensure that you have all the packages required.
- Run the code using command prompt or PyCharm or any other application.
Usage
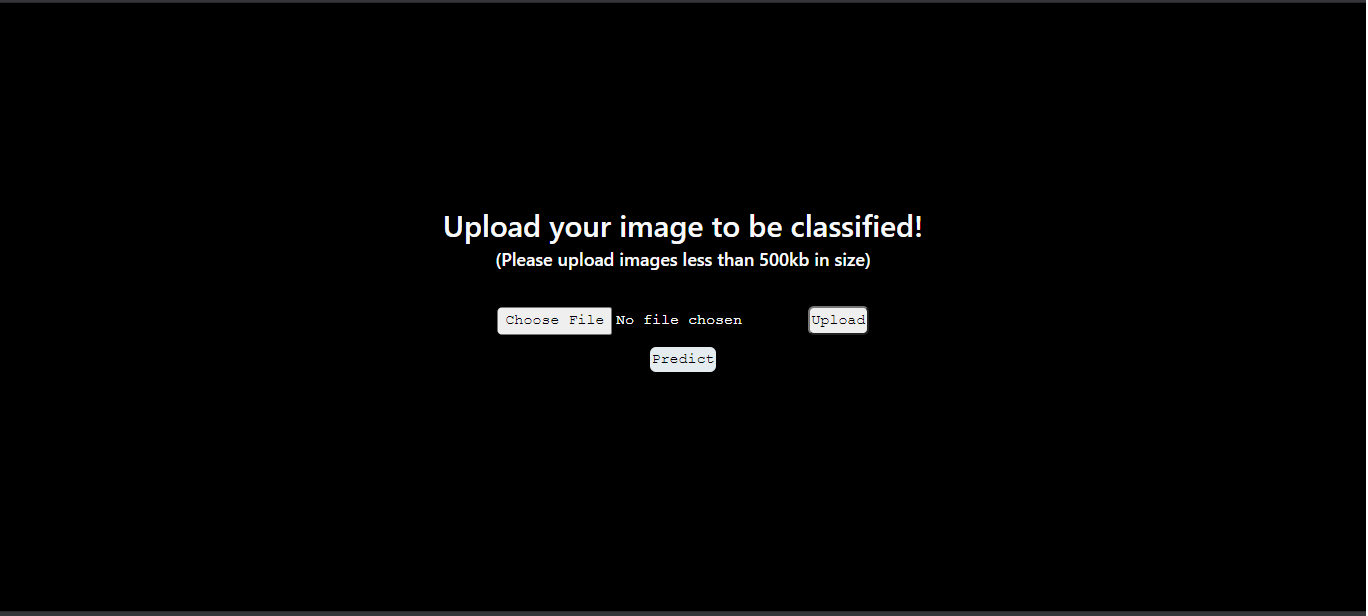
- Click on the ‘Choose File’ button and select a photo.
- Click ‘Upload’ and ‘Predict’ and you have your results.
Applications
- This web application gives the company name, model and year of make of the car just from its car image.
Future scope
- Adding specification and making it into an android app with access to the camera that can help people get details about any car just from its picture.
- It could also give details about nearby dealers using gps.
- An option to search a particular car by name can also be added.
Screenshots